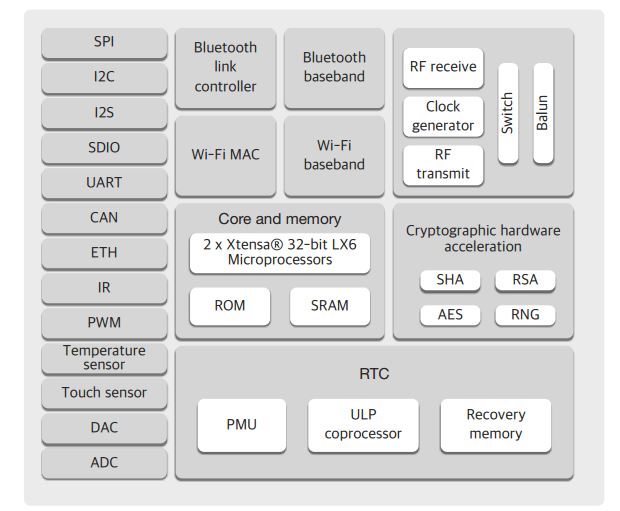
The ESP32 is a low-cost, low-power system on a chip (SoC) series with Wi-Fi & dual-mode Bluetooth capabilities mainly addressed to mobile devices, wearable electronics, and IoT applications. The table and the figure below show the ESP32 main features and internal block diagram. More details can be found here or here.
ESP32 main features
| Number of cores | 2 (dual core)/s |
| Wi-Fi | 2.4 GHz up to 150 Mbits/s |
| Bluetooth | BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) and legacy Bluetooth |
| Architecture/td> | 32 bits |
| Clock frequency | Up to 240 MHz |
| RAM | 512 KB |
| Pins | 30 or 36 (depends on the model) |
| Peripherals | Capacitive touch, ADC (analog to digital converter), DAC (digital to analog converter), I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit), UART (universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter), CAN 2.0 (Controller Area Netwokr), SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface), I2S (Integrated Inter-IC Sound), RMII (Reduced Media-Independent Interface), PWM (pulse width modulation), and more. |
ESP32 Function Block diagram
To use EPS32 to control/sense actuator and sensors using WiFi network there are basically two methods:
- implement a WEB server on the board itself
- exploit the possibility of Firebase Realtime Database to save/update the board GPIO states.
The second option is generally preferable as it allows to control the device from anywhere, simplify the app design, app access require authentication (e-mail and password) but the environment setup require to install several packages.